Product Description
Polaris 25G4108&3211196 DRIVE BELT fits the following models and components:
Polaris Accessories Ranger Vehicles Belts
Polaris Accessories GENERAL Vehicles View All
Aftermarket Parts Drive Belts and Pulleys Drive Belt
Polaris Side by Side 2017 RANGER 1000 XP ALL OPTIONS – R17RT_99 (R24) Drive Train, Clutch, Secondary, Ebs R17rte99a9/B9
Polaris Side by Side 2017 RANGER CREW 1000XP 6P,PS,NB,MD – R17RVE99NY Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2017 RANGER CREW 1000XP PS – R17RVA99A1-E99A9-E99AS-E99AY-M99AM-U99AV Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2017 GENERAL 1000 4P MD – R17RHE99NU Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2017 GENERAL 1000 PS MD – R17RGE99NM-NW Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2017 GENERAL 1000 EPS – R17RGE99A7-A9-AW-AM-KAK Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2016 GENERAL 1000 EPS – R16RGE99A7-AE-AV Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2017 GENERAL 1000 4P PS – R17RHE99AU Drive Train, Secondary Clutch
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 4P PS RC (R03) – G20G4D99AS-BS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20G4D99AS/BS
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 4P EPS EU (R02) – G20G4E99NG DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20G4E99NG
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 4P DLX OPT1 (R02) – G20G4J99AS-BS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20G4J99AS/BS
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 4P PREM. (R03) – G20G4P99AX-BX-ELX DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20G4P99AX/BX/ELX
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 EPS DLX (R04) – G20GAE99A2-A4-D99AK-AS-BK-BS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20GAE99A2/A4/D99AK/AS/BK/BS
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DLX ABS EPS EU TR ZUG (R02) – G20GAE99F2/EFS/BFM/BCM/SFS/SC2 DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20GAE99F2/EFS/BFM/BCM/SFS/SC2
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DLX RC (R02) – G20GAJ99AK-AS-BK-BS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20GAJ99AK/AS/BK/BS
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 PREM (R03) – G20GAP99AM-BM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G20GAP99AM/BM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 DELUXE (R02) – G21G4D99AW/BW DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21G4D99AW/BW
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 DELUXE EU (R01) – G21G4E99NW DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21G4E99NW
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 RC EDITION (R03) – G21G4J99AW/BW DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21G4J99AW/BW
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 PREMIUM EPS (R02) – G21G4P99AM/BM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21G4P99AM/BM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE EPS EU (R01) – G21GAB99CM/FM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21GAB99CM/FM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE EPS (R03) – G21GAD99AC/AW/BC/BW DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21GAD99AC/AW/BC/BW
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 SPORT EPS (R02) – G21GAE99A4 DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21GAE99A4
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE RC (R03) – G21GAJ99AC/AW/BC/BW DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21GAJ99AC/AW/BC/BW
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 PREMIUM EPS (R03) – G21GAP99AM/BM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G21GAP99AM/BM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 DELUXE EU (R01) – G22G4E99NP DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22G4E99NP
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 RC EDITION (R02) – G22G4J99AP/BP DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22G4J99AP/BP
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 4 1000 PREMIUM EPS (R02) – G22G4P99AM/BM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22G4P99AM/BM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE EPS EU (R01) – G22GAB99CP/FP DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22GAB99CP/FP
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE EPS (R01) – G22GAD99AP/BP DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22GAD99AP/BP
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 SPORT EPS (R02) – G22GAE99A4 DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22GAE99A4
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 DELUXE RC (R01) – G22GAJ99AP/BP DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22GAJ99AP/BP
Polaris Side by Side 2571 GENERAL 1000 PREMIUM EPS (R01) – G22GAP99AM/BM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – G22GAP99AM/BM
Polaris Side by Side 2018 GENERAL 1000 4P PS – R18RHE99BK-K99BS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R189RHE99BK
Polaris Side by Side 2018 GENERAL 1000 4P MD – R18RHE99NK DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R189RHE99NK
Polaris Side by Side 2018 GENERAL 1000 EPS – R18RGE99BM-BB-B7-KBS-UB9-BG DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R18RGE99BM/BB/B7/KBS/UB9/UBG
Polaris Side by Side 2018 GENERAL 1000 PS MD – R18RGE99FM-EFB-SCM-SCB-SFM-CCM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R18RGE99FM/EFB/SCM/SCB/SFM/CCM
Polaris Side by Side 2018 RANGER CREW 1000XP PS MD – R18RVE99NX DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R18RVE99NX
Polaris Side by Side 2018 RANGER CREW 1000 PS – R18RVU99AS DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R18RVU99AS
Polaris Side by Side 2019 GENERAL 1000 EPS – R19RGE99A2-EAR-EBR-UAF-UBF-UAM-UBM-UA9-UB9-UAL-UBL-KAK- DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R19RGE99A2/EAR/EBR/UAF/UBF/UAM/UBM/UA9/UB9/UAL/UBL/KAK/
Polaris Side by Side 2019 POLARIS GENERAL 1000 EPS – R19RG_99A2-AR-BR-AF-BF-AM-BM-A9-B9-AL-BL-AK-BK DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R19RGE99A2/EAR/EBR/UAF/UBF/UAM/UBM/UA9/UB9/UAL/UBL/KAK/
Polaris Side by Side 2019 GENERAL 1000 EPS EU TR ZUG MD – R19RGE99F2-FF-SC2-SFF-PCF-PFF DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R19RGE99F2/FF/SC2/SFF/PCF/PFF
Polaris Side by Side 2019 GENERAL 1000 4P PS RC – R19RHE99AD-BD-LD-K99AK-BK DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R19RHE99AD/BD/LD/KAK/BK
Polaris Side by Side 2019 POLARIS GENERAL 1000 4P EPS EU (R01) – R19RHE99ND DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – R19RHE99ND
Polaris Side by Side 2019 RZR 1000S4 – Z19VCE99AM DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – Z19VCE99AM
Polaris Side by Side 2571 RZR 1000S4 (R02) – Z20A4E99AH-LH-BH DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – Z20A4E99AH/LH/BH
Polaris Side by Side 2571 RZR 1000S4 (R01) – Z21A4E99AX/BX DRIVE TRAIN, SECONDARY CLUTCH – Z21A4E99AX/BX
Polaris Side by Side 2017 RANGER CREW 1000XP PS ALL OPTIONS – R17RV_99 Drive Train, Secondary Clutch All Options
Polaris Side by Side 2017 RANGER 1000 XP ALL OPTIONS – R17RT_99 (R24) Drive Train, Secondary Clutch R17rt_99 All Options
Different parts of the drive shaft
The driveshaft is the flexible rod that transmits torque between the transmission and the differential. The term drive shaft may also refer to a cardan shaft, a transmission shaft or a propeller shaft. Parts of the drive shaft are varied and include:
The driveshaft is a flexible rod that transmits torque from the transmission to the differential
When the driveshaft in your car starts to fail, you should seek professional help as soon as possible to fix the problem. A damaged driveshaft can often be heard. This noise sounds like “tak tak” and is usually more pronounced during sharp turns. However, if you can’t hear the noise while driving, you can check the condition of the car yourself.
The drive shaft is an important part of the automobile transmission system. It transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which then transfers it to the wheels. The system is complex, but still critical to the proper functioning of the car. It is the flexible rod that connects all other parts of the drivetrain. The driveshaft is the most important part of the drivetrain, and understanding its function will make it easier for you to properly maintain your car.
Driveshafts are used in different vehicles, including front-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and front-engine rear-wheel drive. Drive shafts are also used in motorcycles, locomotives and ships. Common front-engine, rear-wheel drive vehicle configurations are shown below. The type of tube used depends on the size, speed and strength of the drive shaft.
The output shaft is also supported by the output link, which has 2 identical supports. The upper part of the drive module supports a large tapered roller bearing, while the opposite flange end is supported by a parallel roller bearing. This ensures that the torque transfer between the differentials is efficient. If you want to learn more about car differentials, read this article.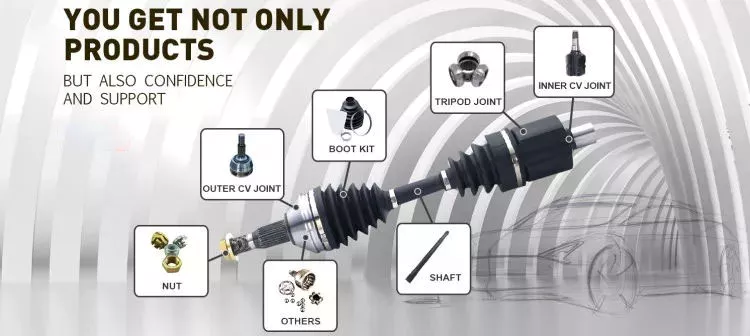
It is also known as cardan shaft, propeller shaft or drive shaft
A propshaft or propshaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotation or torque from an engine or transmission to the front or rear wheels of a vehicle. Because the axes are not directly connected to each other, it must allow relative motion. Because of its role in propelling the vehicle, it is important to understand the components of the driveshaft. Here are some common types.
Isokinetic Joint: This type of joint guarantees that the output speed is the same as the input speed. To achieve this, it must be mounted back-to-back on a plane that bisects the drive angle. Then mount the 2 gimbal joints back-to-back and adjust their relative positions so that the velocity changes at 1 joint are offset by the other joint.
Driveshaft: The driveshaft is the transverse shaft that transmits power to the front wheels. Driveshaft: The driveshaft connects the rear differential to the transmission. The shaft is part of a drive shaft assembly that includes a drive shaft, a slip joint, and a universal joint. This shaft provides rotational torque to the drive shaft.
Dual Cardan Joints: This type of driveshaft uses 2 cardan joints mounted back-to-back. The center yoke replaces the intermediate shaft. For the duplex universal joint to work properly, the angle between the input shaft and the output shaft must be equal. Once aligned, the 2 axes will operate as CV joints. An improved version of the dual gimbal is the Thompson coupling, which offers slightly more efficiency at the cost of added complexity.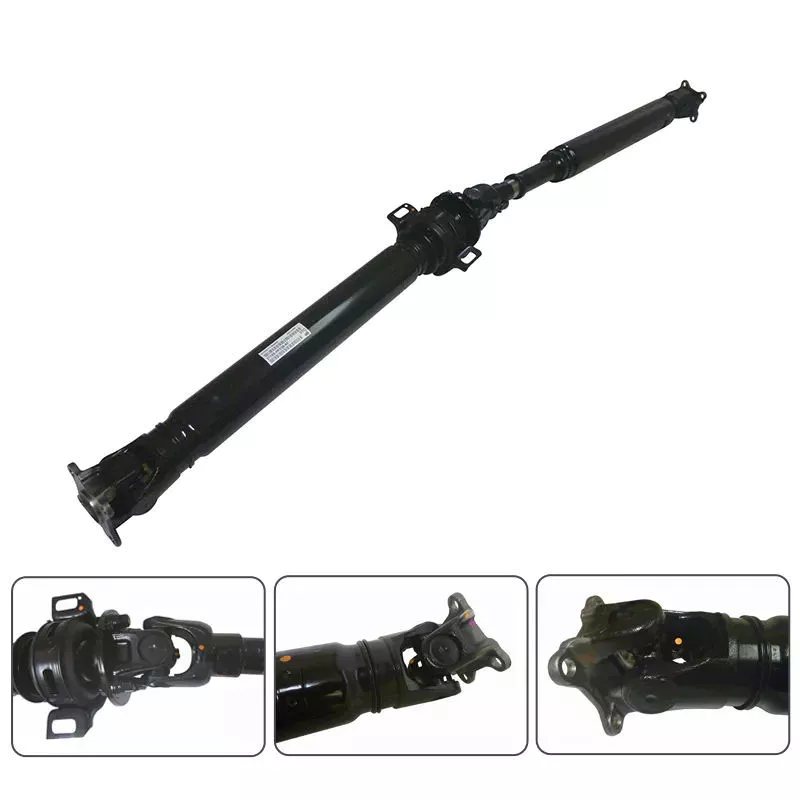
It transmits torque at different angles between driveline components
A vehicle’s driveline consists of various components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels. This includes axles, propshafts, CV joints and differentials. Together, these components transmit torque at different angles between driveline components. A car’s powertrain can only function properly if all its components work in harmony. Without these components, power from the engine would stop at the transmission, which is not the case with a car.
The CV driveshaft design provides smoother operation at higher operating angles and extends differential and transfer case life. The assembly’s central pivot point intersects the joint angle and transmits smooth rotational power and surface speed through the drivetrain. In some cases, the C.V. “U” connector. Drive shafts are not the best choice because the joint angles of the “U” joints are often substantially unequal and can cause torsional vibration.
Driveshafts also have different names, including driveshafts. A car’s driveshaft transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which is then distributed to other driveline components. A power take-off (PTO) shaft is similar to a prop shaft. They transmit mechanical power to connected components. They are critical to the performance of any car. If any of these components are damaged, the entire drivetrain will not function properly.
A car’s powertrain can be complex and difficult to maintain. Adding vibration to the drivetrain can cause premature wear and shorten overall life. This driveshaft tip focuses on driveshaft assembly, operation, and maintenance, and how to troubleshoot any problems that may arise. Adding proper solutions to pain points can extend the life of the driveshaft. If you’re in the market for a new or used car, be sure to read this article.
it consists of several parts
“It consists of several parts” is 1 of 7 small prints. This word consists of 10 letters and is 1 of the hardest words to say. However, it can be explained simply by comparing it to a cow’s kidney. The cocoa bean has several parts, and the inside of the cocoa bean before bursting has distinct lines. This article will discuss the different parts of the cocoa bean and provide a fun way to learn more about the word.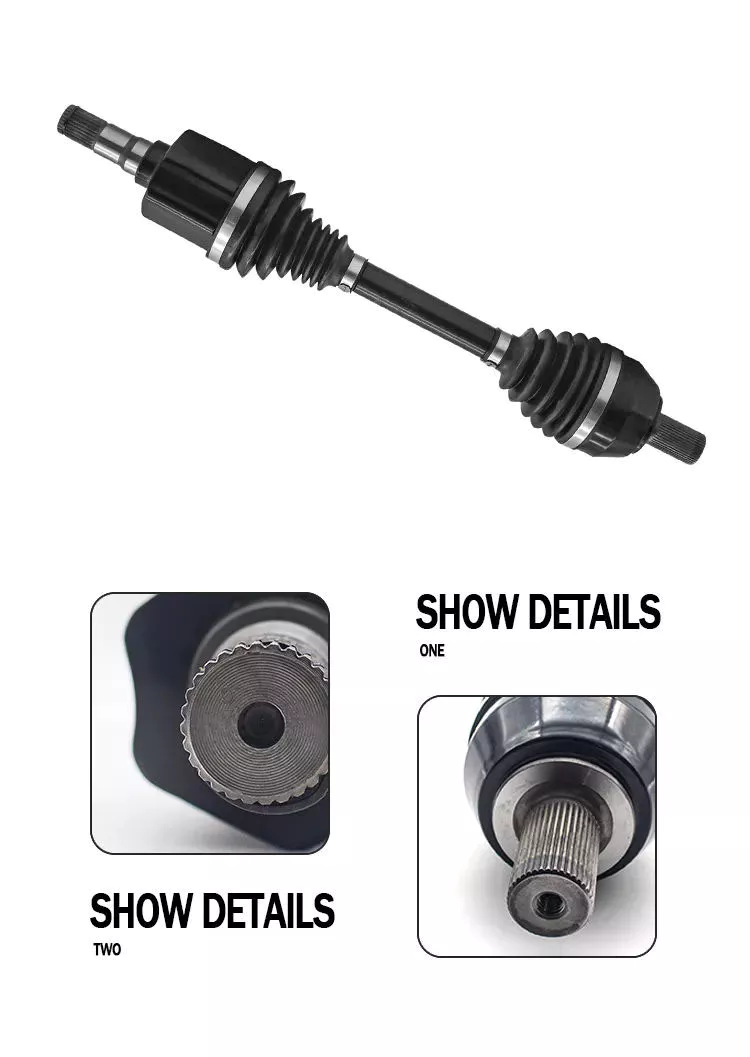
Replacement is expensive
Replacing a car’s driveshaft can be an expensive affair, and it’s not the only part that needs servicing. A damaged drive shaft can also cause other problems. This is why getting estimates from different repair shops is essential. Often, a simple repair is cheaper than replacing the entire unit. Listed below are some tips for saving money when replacing a driveshaft. Listed below are some of the costs associated with repairs:
First, learn how to determine if your vehicle needs a driveshaft replacement. Damaged driveshaft components can cause intermittent or lack of power. Additionally, improperly installed or assembled driveshaft components can cause problems with the daily operation of the car. Whenever you suspect that your car needs a driveshaft repair, seek professional advice. A professional mechanic will have the knowledge and experience needed to properly solve the problem.
Second, know which parts need servicing. Check the u-joint bushing. They should be free of crumbs and not cracked. Also, check the center support bearing. If this part is damaged, the entire drive shaft needs to be replaced. Finally, know which parts to replace. The maintenance cost of the drive shaft is significantly lower than the maintenance cost. Finally, determine if the repaired driveshaft is suitable for your vehicle.
If you suspect your driveshaft needs service, make an appointment with a repair shop as soon as possible. If you are experiencing vibration and rough riding, driveshaft repairs may be the best way to prevent costly repairs in the future. Also, if your car is experiencing unusual noise and vibration, a driveshaft repair may be a quick and easy solution. If you don’t know how to diagnose a problem with your car, you can take it to a mechanic for an appointment and a quote.

